Relativistic electromagnetism
Static magnetic field
Edward M. Purcell Electricity and Magnetism, Berkeley Physics Course, Vol. 2 in SI units
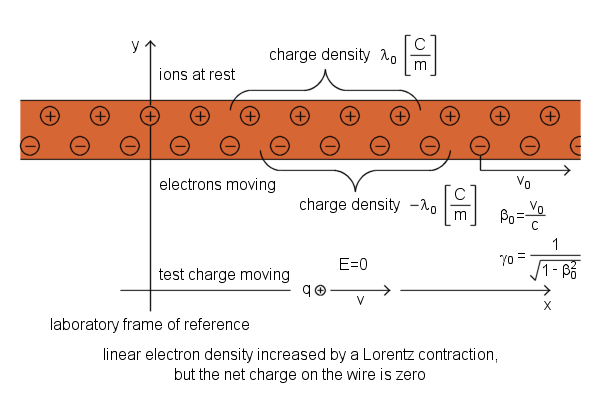
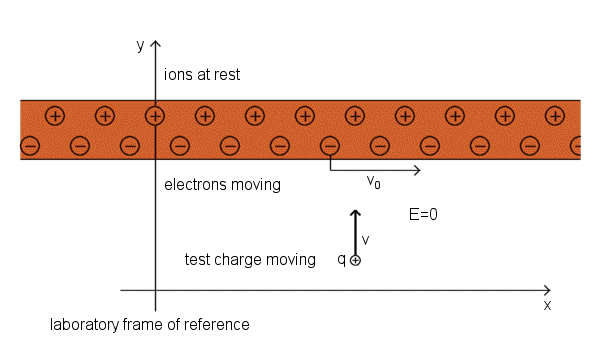
Current-Carrying Wire, positive ions and electrons are shown separated for clarity
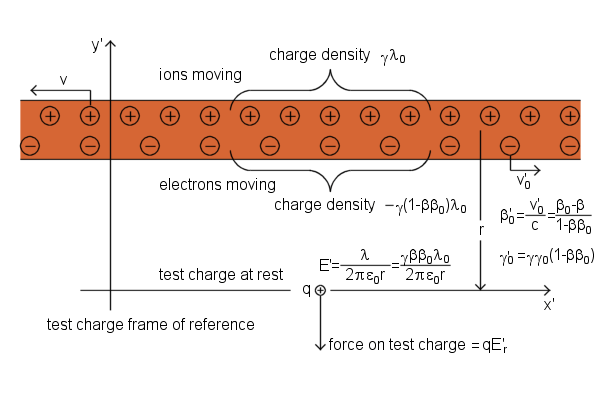
Current-Carrying Wire, positive ions and electrons are shown separated for clarity
The linear density of positive charge in the test charge frame is
γλ0
Calculation of the linear density of negative charge in the test charge frame:
The electron linear density in the lab frame, which was - λ0, had already been increased by a Lorentz contraction.
Thus the linear density of negative charge in the electrons' own rest frame must have been
- λ0/γ0
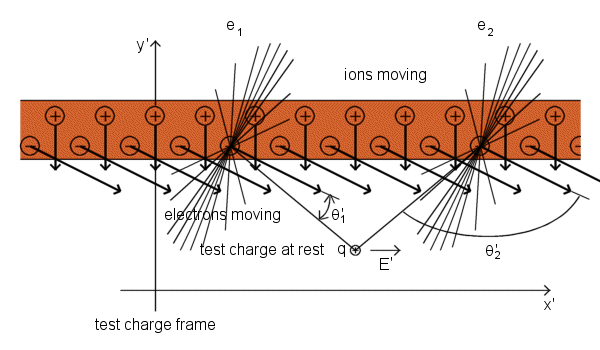
Now we calculate the speed of the electrons in the test charge frame in order to calculate their density there:
Relativistic formula for the addition of velocities![]()
![]()
![]()
Lorentz factor![]()
The total linear density of charge in the wire in the test charge frame![]()
A radial electric field of infinite line charge![]()
Force on test charge![]()
For the observer in the test charge frame wire is length contracted
Return to the lab frame![]()
The total current I in the wire
- λ0v0 or - λ0β0c
Force on test charge![]()
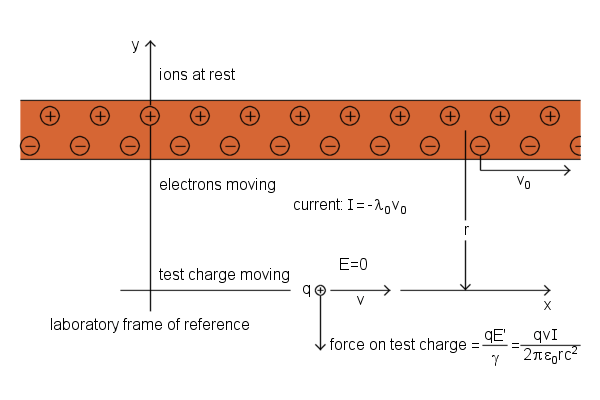
Current-Carrying Wire, positive ions and electrons are shown separated for clarity